PR Agent Dashboard
The PR Agent Dashboard enables users to manage access permissions, automate PR response generation, and gain insights through analytical graphs and pull request history tracking. It helps efficiently monitor, manage, and optimize pull request activities, code quality, and security across repositories for improved review processes.
1) View Pull Request Permissions and Summary Generation
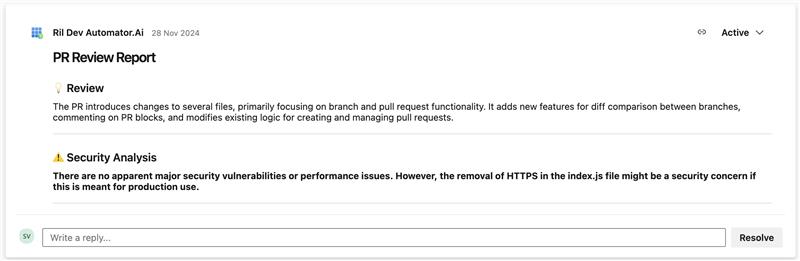
a. After each pull request is created, the PR Agent page automatically generates graphical summaries, providing insights into the PR activity, including code quality, security, and review metrics.
b. Go to the PR Agent section within your project. Access to and modifications on this page are controlled on a project-by-project basis and are restricted to designated users, specifically the Project Lead or Admin.
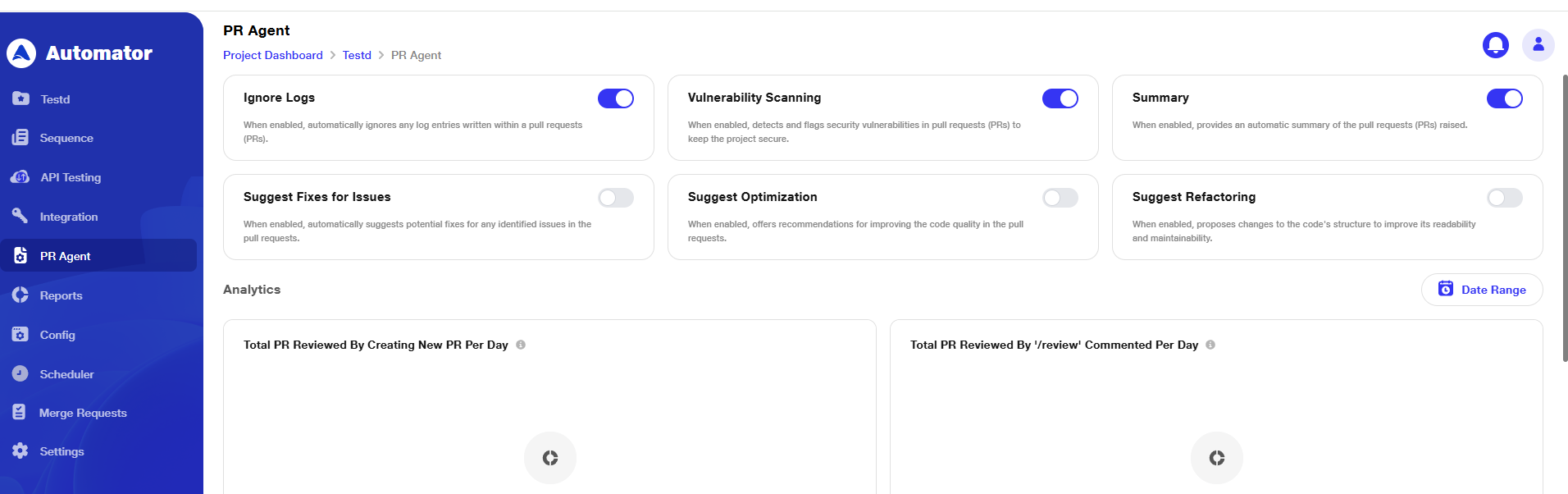
2) Manage Pull Request Permissions
a. The options Ignore Logs, Vulnerability Scanning, Summary, Suggest Fixes for Issues, Suggest Optimization, and Suggest Refactoring allow users to manage what information is included in the reports generated after a pull request is raised.
b. These settings control the type of data reflected in the PR analysis based on the permissions and preferences set by the user.
c. By default, in the configuration settings, Ignore Logs and Vulnerability Scanning are turned ON, while the other configuration options are turned OFF.
d. To make changes, toggle the switch on or off as needed.
e. Once a pull request is raised, a report is generated based on the enabled settings, including only the relevant data.
f. Understand the toggle buttons functions as described below:
i. Ignore Logs: When the Ignore Logs, option is enabled; any log entries within a pull request (PR) are automatically excluded from the report. This helps streamline the review process by filtering out log information that may not be relevant to the actual code changes. This toggle button is ON by default.
ii. Vulnerability Scanning: When the Vulnerability Scanning option is enabled, the system automatically scans the project's dependency files for known security vulnerabilities. This helps ensure project security by identifying and flagging any outdated or vulnerable libraries. This toggle button is ON by default.
iii. Summary: When the Summary option is enabled, an automatic summary of the raised pull request (PR) is generated. This summary highlights key changes, updates, and additions, helping reviewers quickly understand the purpose and impact of the PR. This toggle button is OFF by default.
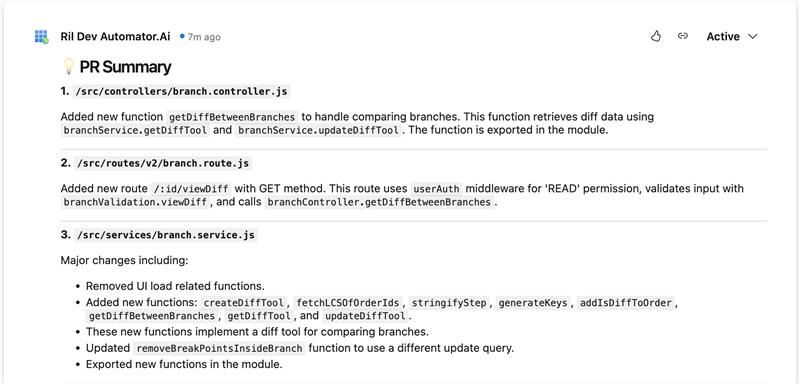
iv Suggest Fixes for Issues: When the Suggest Fixes for Issues option is enabled, the system automatically suggests potential fixes for any identified issues in the pull request. This helps streamline the review process by offering actionable recommendations to resolve errors and enhance code quality. This toggle button is OFF by default.
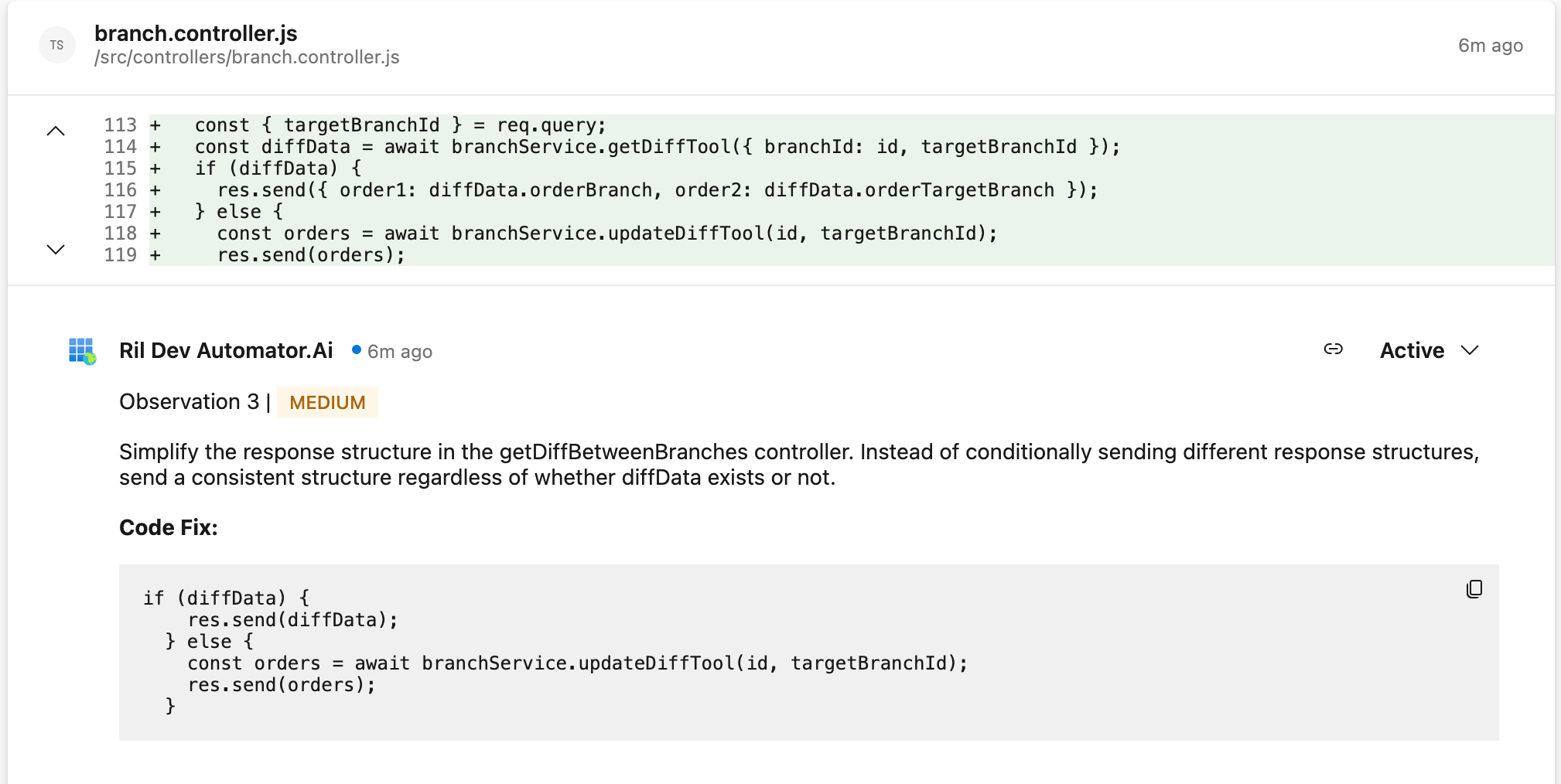
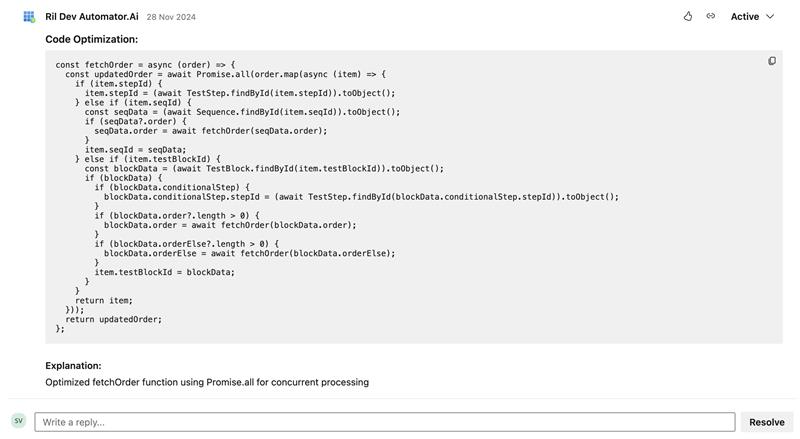
v. Suggest Optimization: When the Suggest Optimization option is enabled, the system provides recommendations to enhance code quality within the pull request. These suggestions may include performance optimizations, refactoring opportunities, or adherence to best practices aimed at improving readability, maintainability, and overall efficiency. This toggle button is OFF by default.
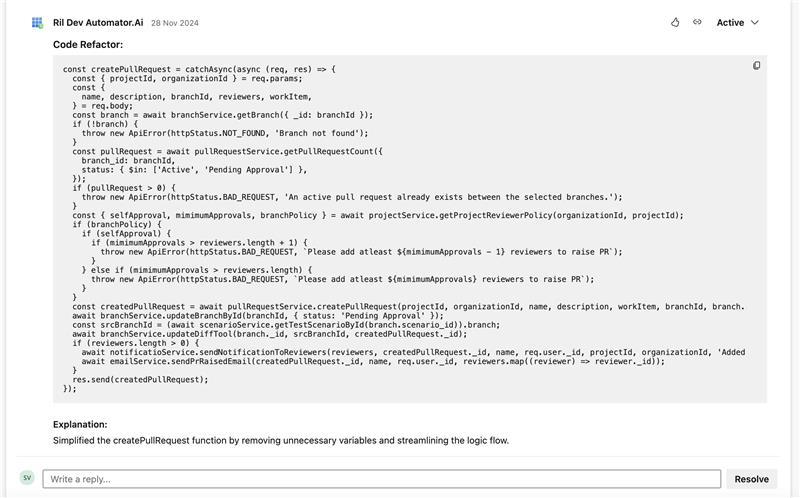
vi. Suggest Refactoring: When the Suggest Refactoring option is enabled, the system proposes structural changes to the code to enhance readability and maintainability. These suggestions may include reorganizing logic, simplifying complex functions, or improving code clarity—without changing the code’s overall functionality. This toggle button is OFF by default.
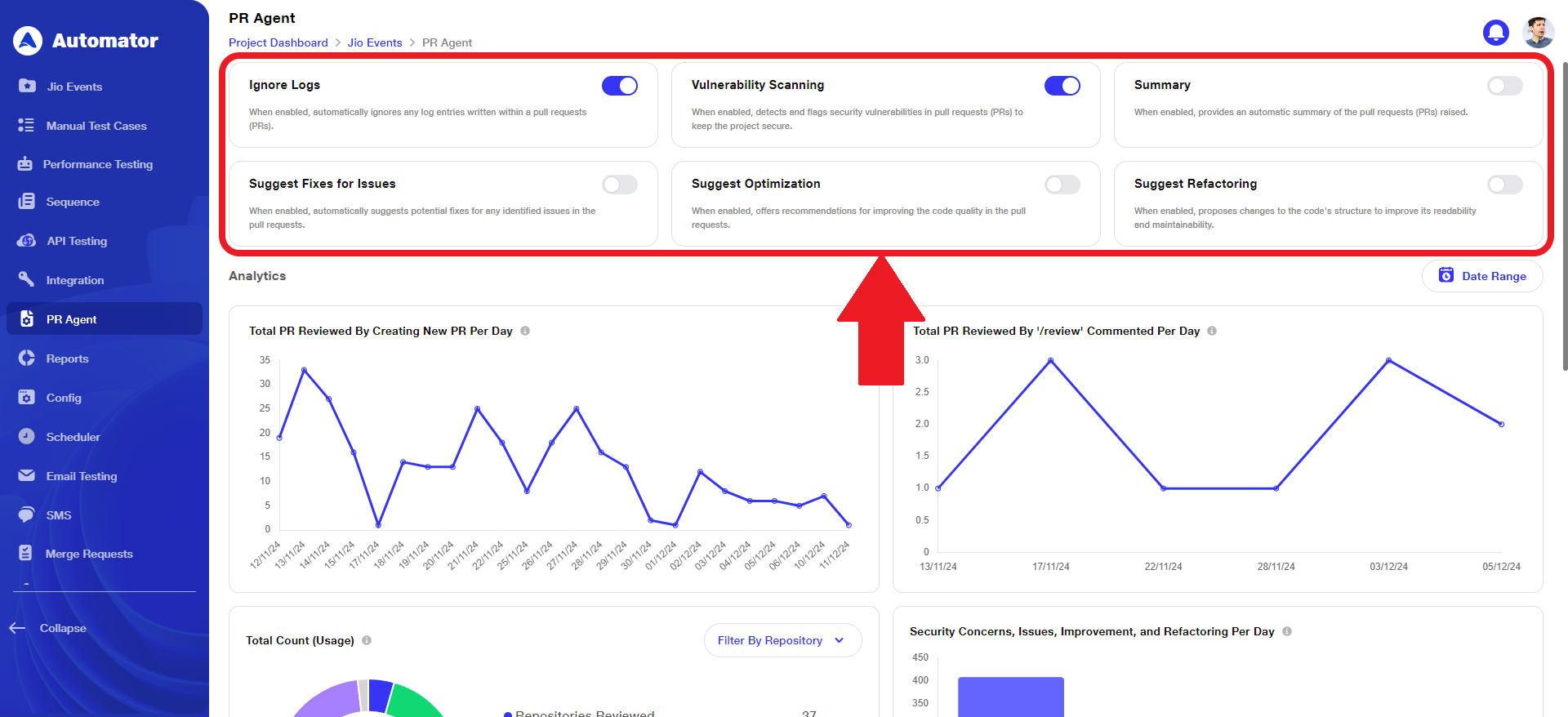
3) View Graphical Summary
a. Graphical summaries are available for the following metrics: Total PRs Reviewed by Creating New PRs Per Day, Total PRs Reviewed Using the '/review' Comment Per Day, Total Count (Usage), and Security Concerns, Issues, Improvements, and Refactoring Per Day.
b. By default, the date range for the graphical view is set to a past 1-week period.
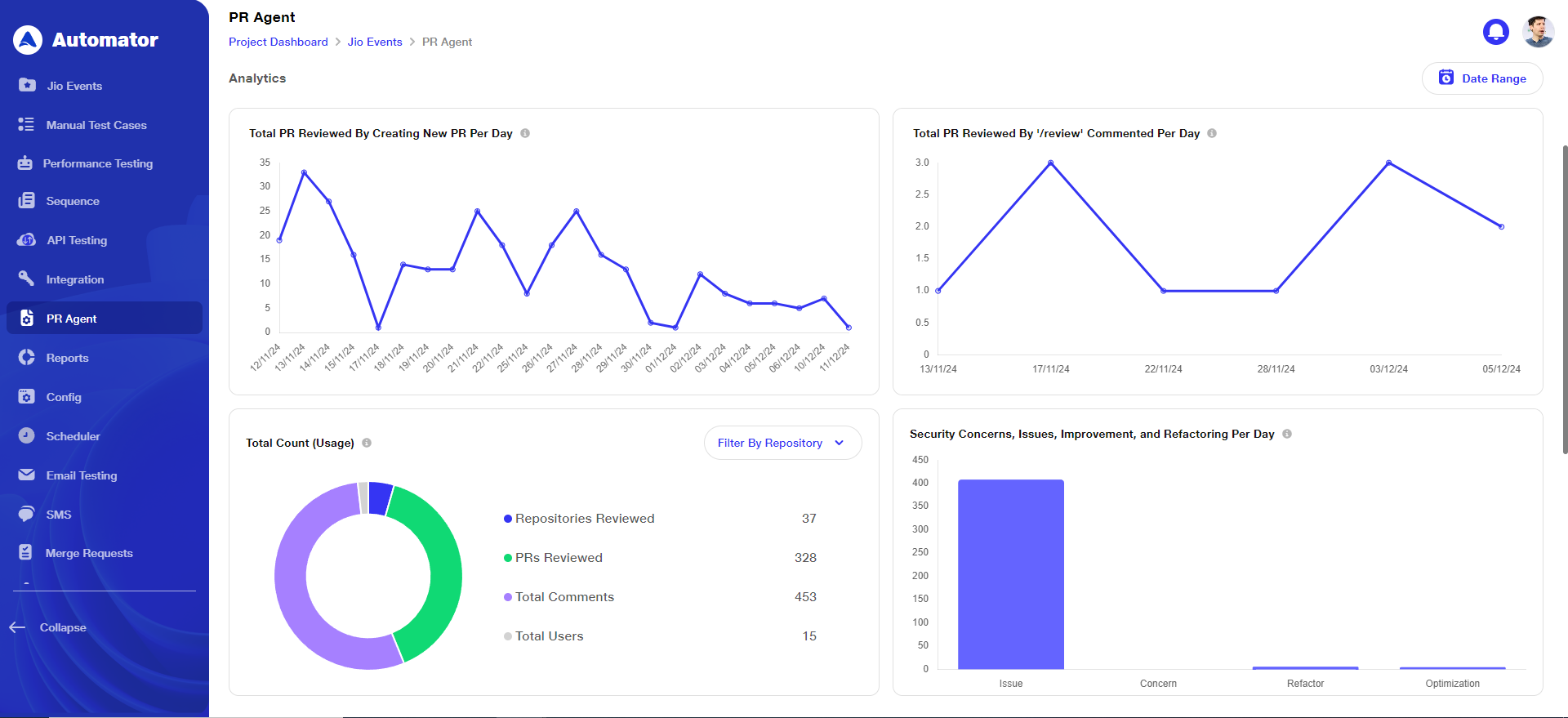
c. The graphs are defined as follows:
1. Total PR Reviewed By Creating New PR Per Day: This metric tracks the number of pull requests (PRs) reviewed daily by generating new PRs. It helps monitor the team’s code review productivity by measuring how frequently new PRs are created and assessed each day.
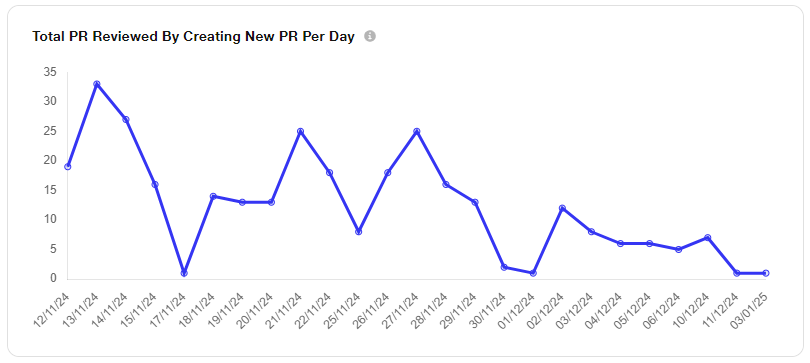
ii. Total PR Reviewed By ‘/review’ Commented Per Day: This metric tracks the number of pull requests (PRs) reviewed daily using the '/review' comment. It helps measure the team’s code review activity and efficiency by monitoring how often the '/review' command is used to indicate a review on PRs.
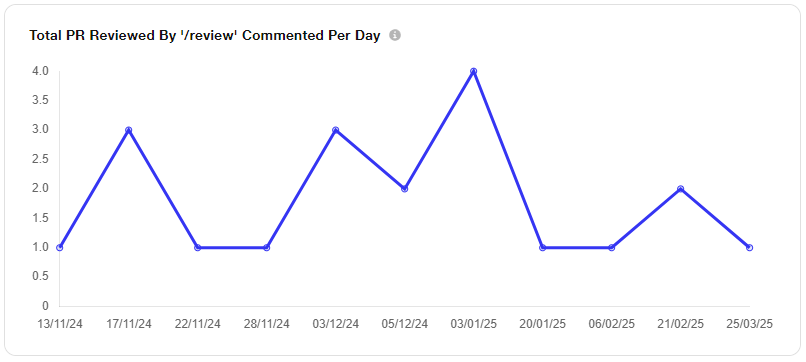
iii. Total Count (Usage): This metric tracks the overall frequency of specific actions or features, such as Repositories Reviewed, PRs Reviewed, Total Comments, and Total Users. It provides insights into the popularity and effectiveness of these processes.
iv. Security Concerns, Issues, Improvement, and Refactoring Per Day: This chart visually tracks the daily count of identified security vulnerabilities, code issues, suggested improvements, and refactoring recommendations. It helps monitor trends over time and provides valuable insights into the overall quality and security of the codebase.
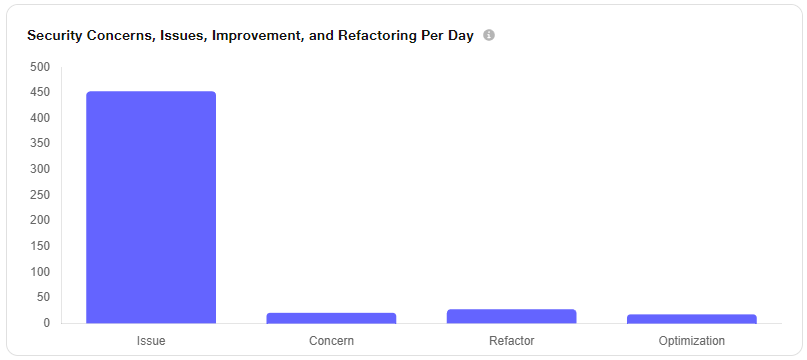
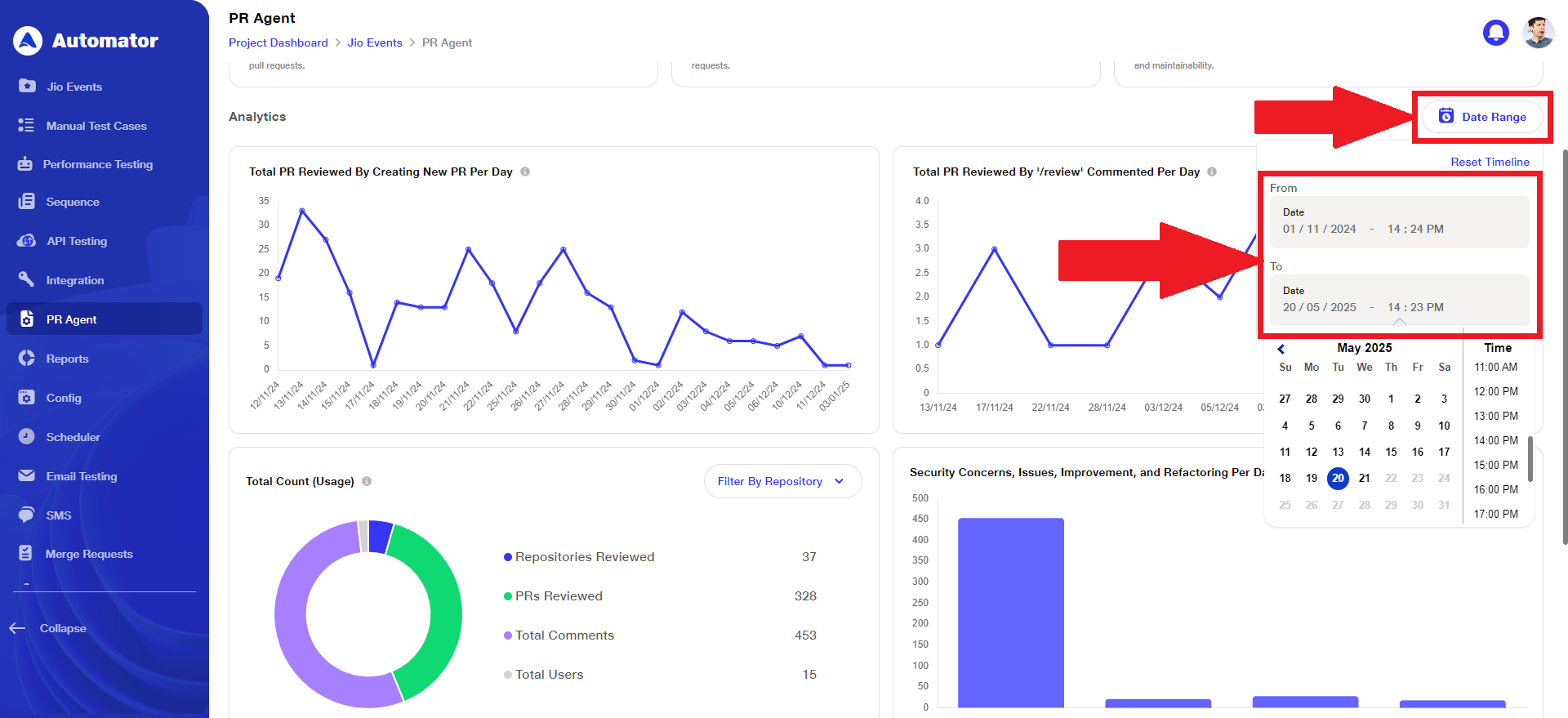
4) Select Data Range
To view data for a specific date range, click on Date Range and specify the From and To dates and times.
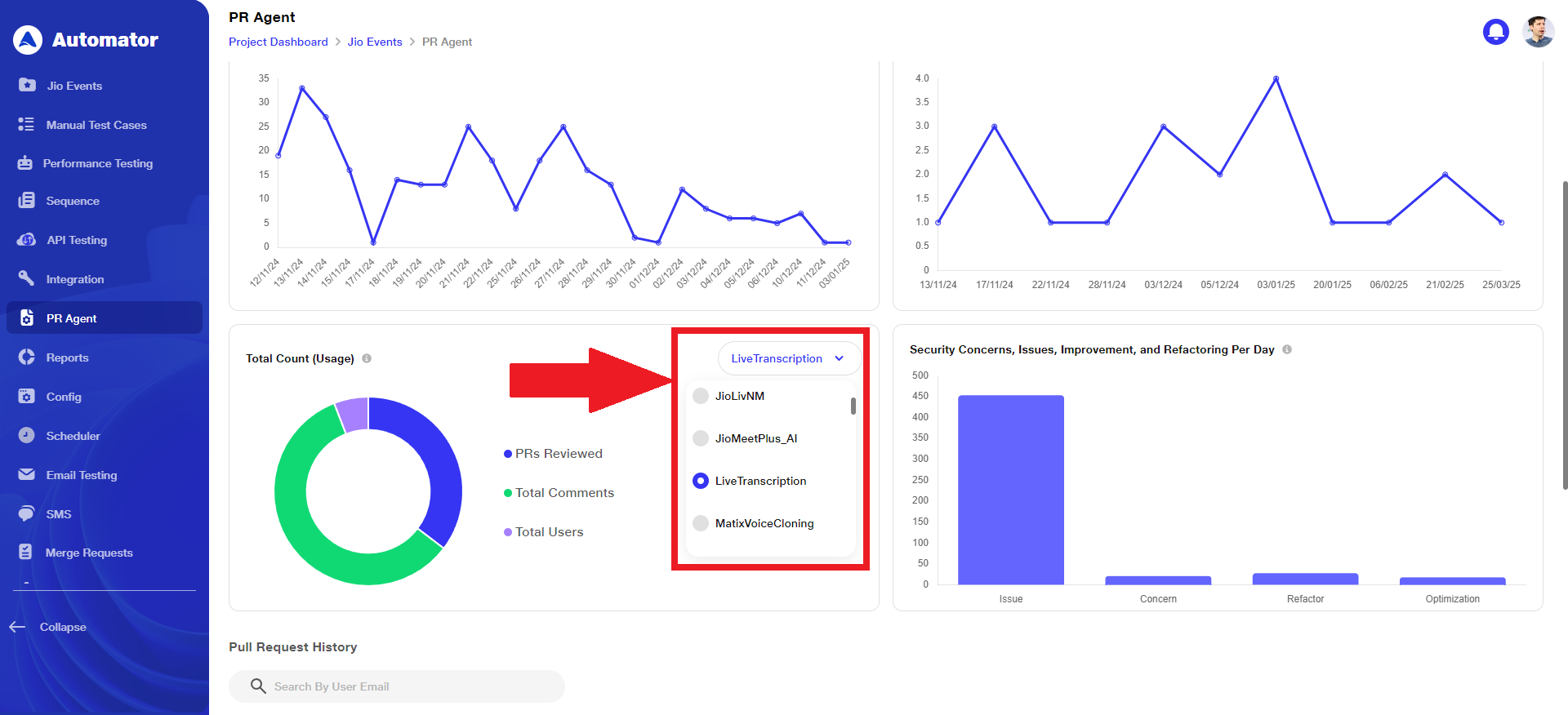
5) Filter By Repository for Total Count (Usage)
a. For the Total Count (Usage) graph, a Filter By Repository option is available through the dropdown menu. Users can choose to view either overall data across all repositories or filter the data based on a specific repository as needed.
b. Once a repository is selected, the label updates to reflect the selected repository name, and the metrics — PRs Reviewed, Total Comments, and Total Users — are displayed accordingly
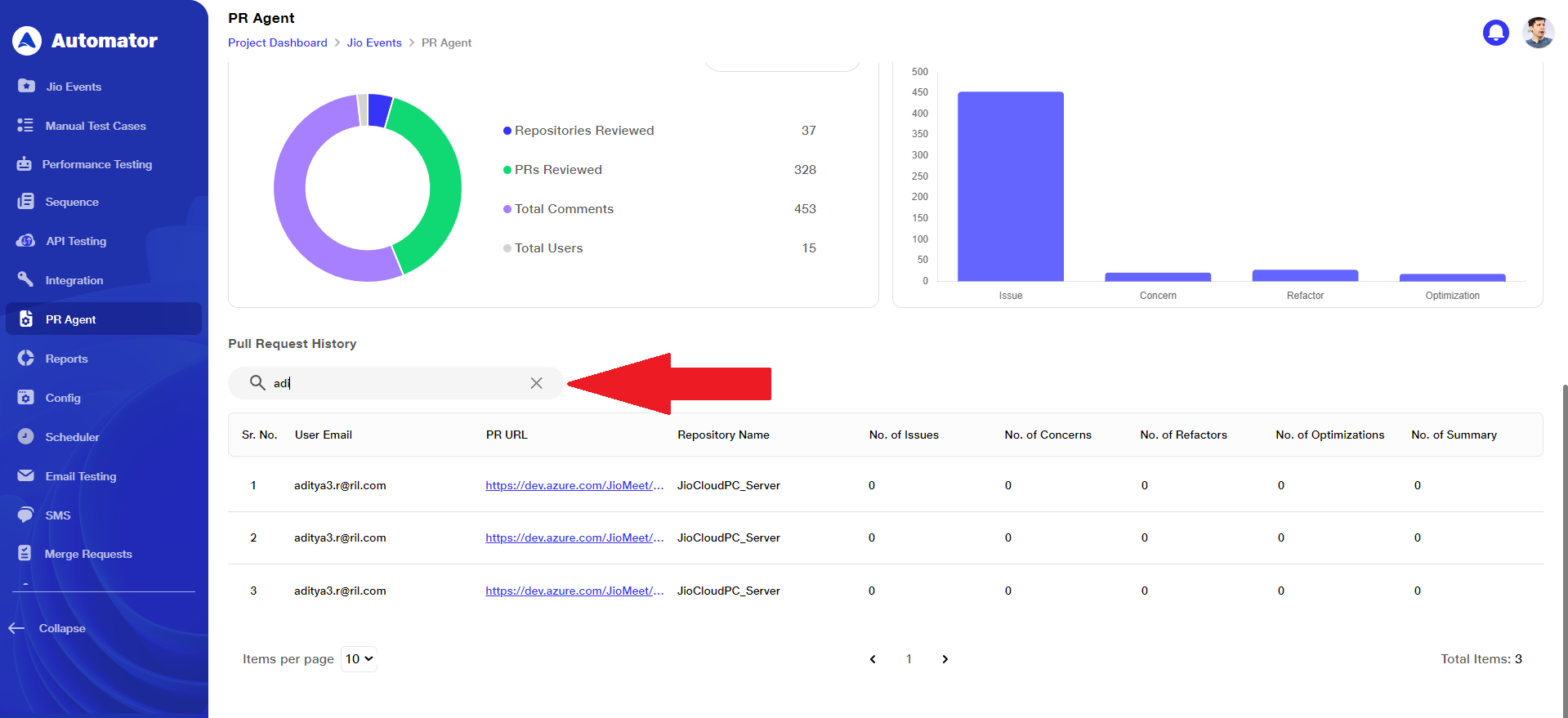
6) View Pull Request History
a. The Pull Request History table lists user emails along with the corresponding PR URLs, repository names, and counts of issues, concerns, refactors, optimizations, and summaries for each respective pull request.
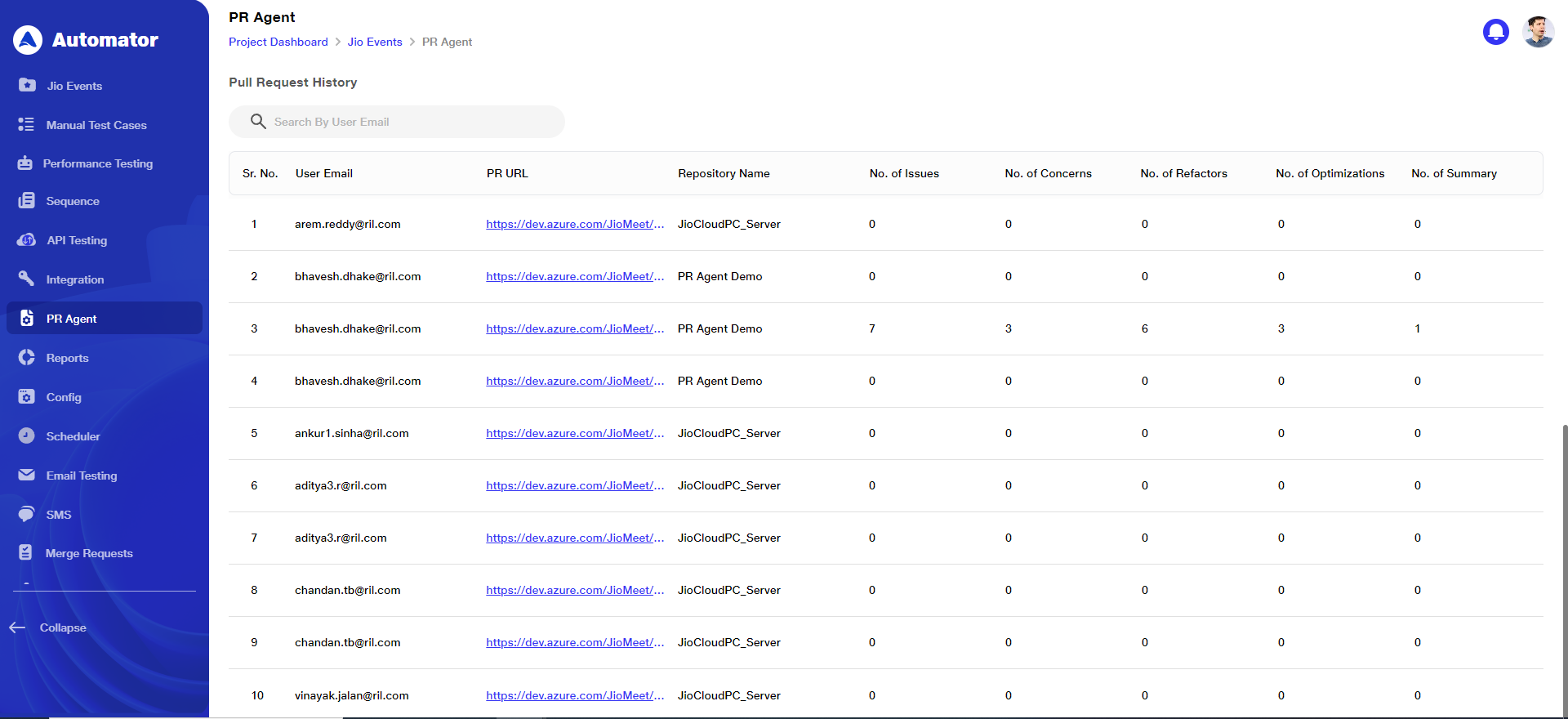
7) Specific User Pull Request History
a. The search option in the Pull Request History allows users to quickly find specific data related to a particular user by entering their email address.